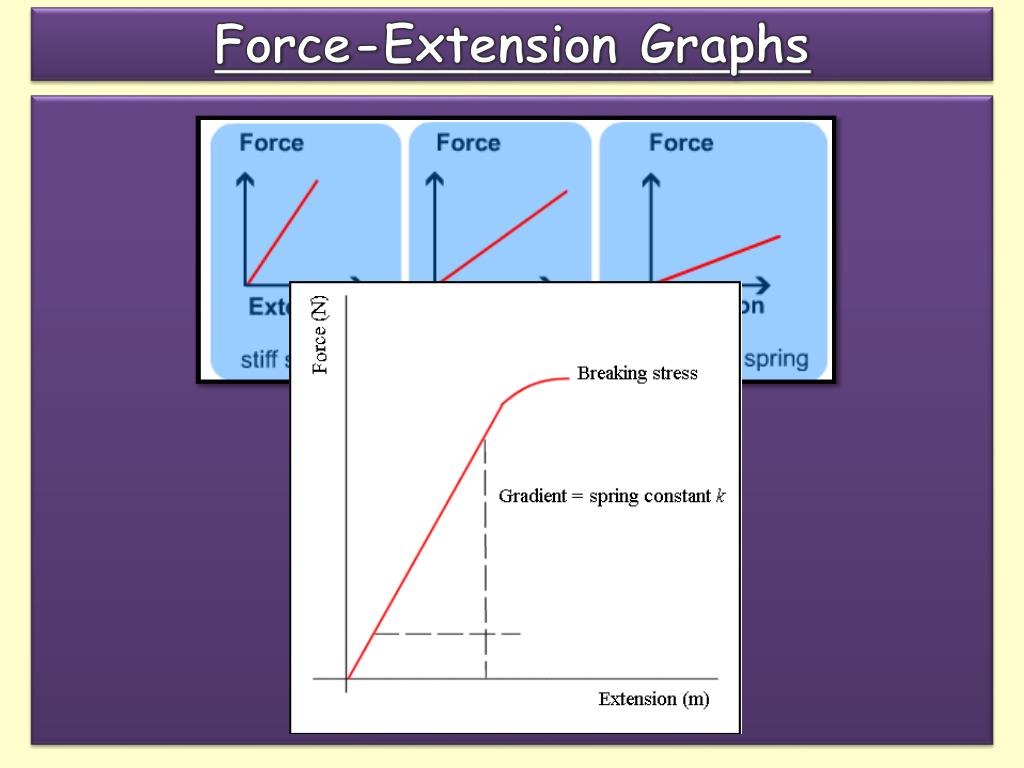
Extension Definition Of Force . hooke’s law states that the force required to extend or compress a spring by some distance is directly proportional to that distance. When we apply force to an elastic object (such as a spring) it will extend. The force will either stretch or compress the object. hooke’s law states that within the elastic limit, the extension (x) of an object is directly proportional to the force (f) that causes. Force (f) is measured in newtons (n) spring constant (k) is. extension occurs due to force. Forces are responsible for changing the motion of object. when a force is applied to an object it can change its size and shape. The extension of an elastic object can be described. force = spring constant × extension. \ (f = k~e\) this is when:
from www.slideserve.com
When we apply force to an elastic object (such as a spring) it will extend. extension occurs due to force. Forces are responsible for changing the motion of object. The extension of an elastic object can be described. hooke’s law states that the force required to extend or compress a spring by some distance is directly proportional to that distance. hooke’s law states that within the elastic limit, the extension (x) of an object is directly proportional to the force (f) that causes. Force (f) is measured in newtons (n) spring constant (k) is. \ (f = k~e\) this is when: when a force is applied to an object it can change its size and shape. The force will either stretch or compress the object.
PPT CIE IGCSE PHYSICS Forces Hookes Law PowerPoint Presentation
Extension Definition Of Force Forces are responsible for changing the motion of object. extension occurs due to force. when a force is applied to an object it can change its size and shape. Forces are responsible for changing the motion of object. \ (f = k~e\) this is when: The extension of an elastic object can be described. Force (f) is measured in newtons (n) spring constant (k) is. force = spring constant × extension. When we apply force to an elastic object (such as a spring) it will extend. The force will either stretch or compress the object. hooke’s law states that within the elastic limit, the extension (x) of an object is directly proportional to the force (f) that causes. hooke’s law states that the force required to extend or compress a spring by some distance is directly proportional to that distance.
From www.perplexity.ai
A ForceExtension Graph for A Levels Physics Extension Definition Of Force The extension of an elastic object can be described. hooke’s law states that within the elastic limit, the extension (x) of an object is directly proportional to the force (f) that causes. force = spring constant × extension. hooke’s law states that the force required to extend or compress a spring by some distance is directly proportional. Extension Definition Of Force.
From www.britannica.com
Elasticity Definition, Examples, & Facts Britannica Extension Definition Of Force Force (f) is measured in newtons (n) spring constant (k) is. Forces are responsible for changing the motion of object. when a force is applied to an object it can change its size and shape. The force will either stretch or compress the object. hooke’s law states that the force required to extend or compress a spring by. Extension Definition Of Force.
From www.youtube.com
AQA GCSE Physics Revision Equation Force, Extension and Sprint Constant Extension Definition Of Force hooke’s law states that the force required to extend or compress a spring by some distance is directly proportional to that distance. when a force is applied to an object it can change its size and shape. Force (f) is measured in newtons (n) spring constant (k) is. The extension of an elastic object can be described. When. Extension Definition Of Force.
From www.youtube.com
Pronunciation of Extension Definition of Extension YouTube Extension Definition Of Force The extension of an elastic object can be described. Force (f) is measured in newtons (n) spring constant (k) is. When we apply force to an elastic object (such as a spring) it will extend. The force will either stretch or compress the object. extension occurs due to force. hooke’s law states that the force required to extend. Extension Definition Of Force.
From www.savemyexams.com
ForceExtension Graphs Edexcel A Level Physics Revision Notes 2017 Extension Definition Of Force hooke’s law states that within the elastic limit, the extension (x) of an object is directly proportional to the force (f) that causes. Forces are responsible for changing the motion of object. force = spring constant × extension. when a force is applied to an object it can change its size and shape. hooke’s law states. Extension Definition Of Force.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Movements PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID443502 Extension Definition Of Force The extension of an elastic object can be described. The force will either stretch or compress the object. When we apply force to an elastic object (such as a spring) it will extend. \ (f = k~e\) this is when: Force (f) is measured in newtons (n) spring constant (k) is. Forces are responsible for changing the motion of object.. Extension Definition Of Force.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT CIE IGCSE PHYSICS Forces Hookes Law PowerPoint Presentation Extension Definition Of Force Forces are responsible for changing the motion of object. extension occurs due to force. \ (f = k~e\) this is when: hooke’s law states that the force required to extend or compress a spring by some distance is directly proportional to that distance. hooke’s law states that within the elastic limit, the extension (x) of an object. Extension Definition Of Force.
From physics.stackexchange.com
elasticity Graph relating load force and spring extension in Hookes Extension Definition Of Force \ (f = k~e\) this is when: force = spring constant × extension. When we apply force to an elastic object (such as a spring) it will extend. Forces are responsible for changing the motion of object. hooke’s law states that the force required to extend or compress a spring by some distance is directly proportional to that. Extension Definition Of Force.
From www.savemyexams.com
Required Practical Investigating Force & Extension AQA GCSE Physics Extension Definition Of Force force = spring constant × extension. extension occurs due to force. when a force is applied to an object it can change its size and shape. \ (f = k~e\) this is when: hooke’s law states that the force required to extend or compress a spring by some distance is directly proportional to that distance. . Extension Definition Of Force.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT CIE IGCSE PHYSICS Forces Hookes Law PowerPoint Presentation Extension Definition Of Force Force (f) is measured in newtons (n) spring constant (k) is. \ (f = k~e\) this is when: extension occurs due to force. force = spring constant × extension. The extension of an elastic object can be described. hooke’s law states that the force required to extend or compress a spring by some distance is directly proportional. Extension Definition Of Force.
From www.numerade.com
SOLVED "1) Based on this graph of force vs. extension for a certain Extension Definition Of Force \ (f = k~e\) this is when: Forces are responsible for changing the motion of object. When we apply force to an elastic object (such as a spring) it will extend. Force (f) is measured in newtons (n) spring constant (k) is. hooke’s law states that within the elastic limit, the extension (x) of an object is directly proportional. Extension Definition Of Force.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT CIE IGCSE PHYSICS Forces Hookes Law PowerPoint Presentation Extension Definition Of Force force = spring constant × extension. when a force is applied to an object it can change its size and shape. hooke’s law states that within the elastic limit, the extension (x) of an object is directly proportional to the force (f) that causes. When we apply force to an elastic object (such as a spring) it. Extension Definition Of Force.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Work and Energy PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID4524294 Extension Definition Of Force force = spring constant × extension. Force (f) is measured in newtons (n) spring constant (k) is. hooke’s law states that the force required to extend or compress a spring by some distance is directly proportional to that distance. Forces are responsible for changing the motion of object. when a force is applied to an object it. Extension Definition Of Force.
From www.savemyexams.com
ForceExtension Graphs OCR A Level Physics Revision Notes 2017 Extension Definition Of Force extension occurs due to force. when a force is applied to an object it can change its size and shape. The force will either stretch or compress the object. hooke’s law states that within the elastic limit, the extension (x) of an object is directly proportional to the force (f) that causes. Force (f) is measured in. Extension Definition Of Force.
From www.slideshare.net
Chapter 10 Force and Pressure Part 1 Extension Definition Of Force extension occurs due to force. hooke’s law states that the force required to extend or compress a spring by some distance is directly proportional to that distance. The extension of an elastic object can be described. force = spring constant × extension. When we apply force to an elastic object (such as a spring) it will extend.. Extension Definition Of Force.
From www.dreamstime.com
Hooke's Law. The Force Is Proportional To The Extension Stock Vector Extension Definition Of Force hooke’s law states that within the elastic limit, the extension (x) of an object is directly proportional to the force (f) that causes. When we apply force to an elastic object (such as a spring) it will extend. force = spring constant × extension. The extension of an elastic object can be described. hooke’s law states that. Extension Definition Of Force.
From educatorpages.com
Physical science overview Extension Definition Of Force Force (f) is measured in newtons (n) spring constant (k) is. extension occurs due to force. The force will either stretch or compress the object. hooke’s law states that within the elastic limit, the extension (x) of an object is directly proportional to the force (f) that causes. The extension of an elastic object can be described. . Extension Definition Of Force.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Muscle movements, types, and names PowerPoint Presentation ID Extension Definition Of Force When we apply force to an elastic object (such as a spring) it will extend. hooke’s law states that the force required to extend or compress a spring by some distance is directly proportional to that distance. force = spring constant × extension. The force will either stretch or compress the object. The extension of an elastic object. Extension Definition Of Force.